1. Load Balancing Solution Architecture
You can configure Foreman server to use a load balancer to distribute client requests and network load across multiple Smart Proxy servers. This results in an overall performance improvement on Smart Proxy servers.
This guide outlines how to prepare Foreman server and Smart Proxy server for load balancing, and provides guidelines on how to configure a load balancer and register clients in a load-balanced setup.
A load-balanced setup consists of the following components:
-
Foreman server
-
Two or more Smart Proxy servers
-
A load balancer
-
Multiple clients
The graphics in this section are Red Hat illustrations. Non-Red Hat illustrations are welcome. If you want to contribute alternative images, raise a pull request in the Foreman Documentation GitHub page. Note that in Red Hat terminology, "Satellite" refers to Foreman and "Capsule" refers to Smart Proxy.
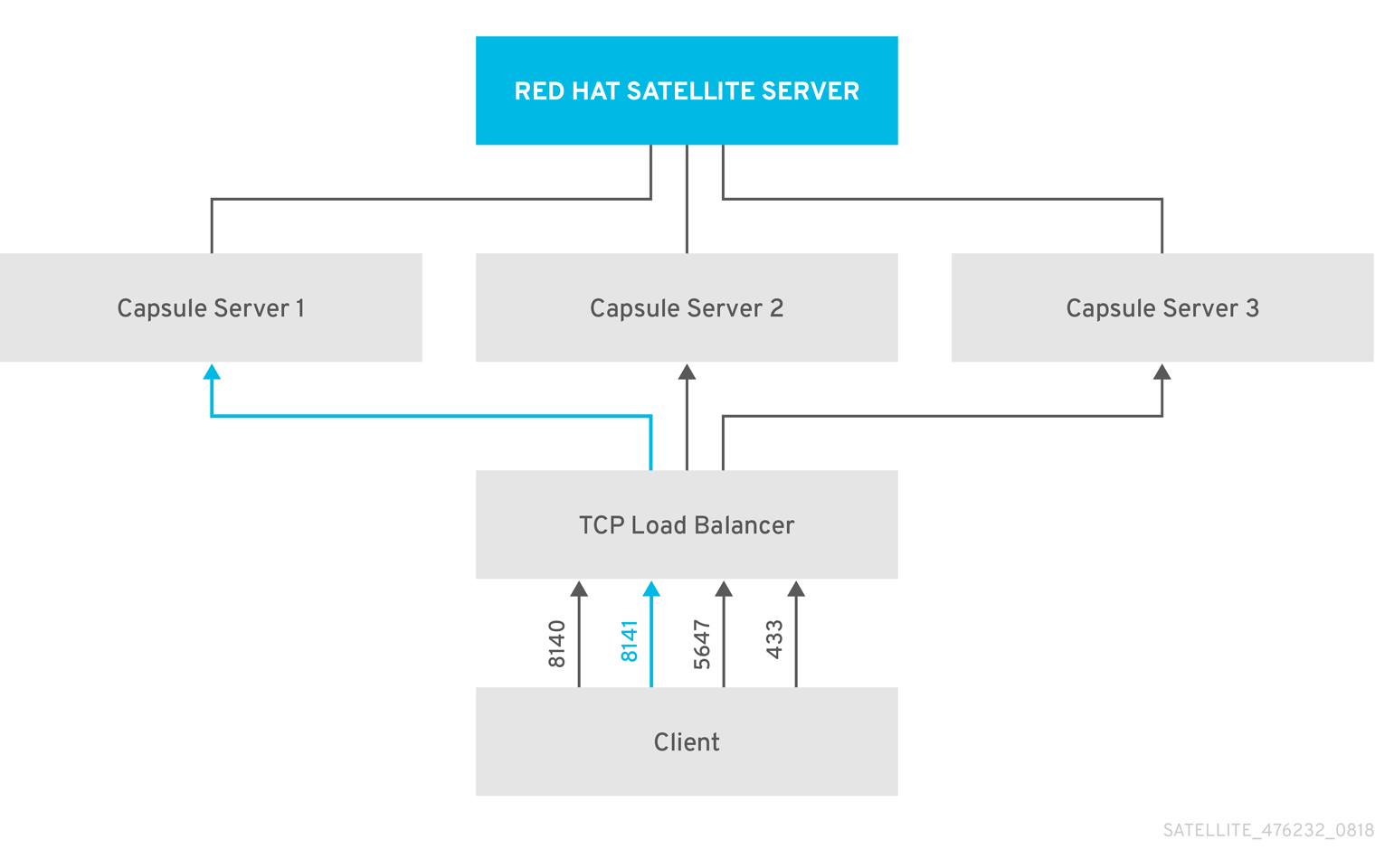
In a load-balanced setup, nearly all Smart Proxy functionality continues to work as expected when one Smart Proxy server is down, for planned or unplanned maintenance. Load balancer works with the following services and features:
-
Registration using
subscription-manager -
Content Management with
yumrepositories -
Optional: Puppet
|
Note
|
In the load-balanced setup, a load balancer distributes load only for the services and features mentioned above. If other services, such as provisioning or virt-who, are running on the individual Smart Proxies, you must access them directly through Smart Proxies and not through the load balancer. |
Puppet Certificate Authority (CA) management does not support certificate signing in a load-balanced setup. Puppet CA stores certificate information, such as the serial number counter and CRL, on the file system. Multiple writer processes that attempt to use the same data can corrupt it.
To manage this Puppet limitation, complete the following steps:
-
Configure Puppet certificate signing on one Smart Proxy server, typically the first system where you configure Smart Proxy server for load balancing.
-
Configure the clients to send CA requests to port 8141 on a load balancer.
-
Configure a load balancer to redirect CA requests from port 8141 to port 8140 on the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates.
2. Load Balancing Considerations
Distributing load between several Smart Proxy servers prevents any one Smart Proxy from becoming a single point of failure. Configuring Smart Proxies to use a load balancer can provide resilience against planned and unplanned outages. This improves availability and responsiveness.
Consider the following guidelines when configuring load balancing:
-
If you use Puppet, Puppet certificate signing is assigned to the first Smart Proxy that you configure. If the first Smart Proxy is down, clients cannot obtain Puppet content.
-
This solution does not use Pacemaker or other similar HA tools to maintain one state across all Smart Proxies. To troubleshoot issues, reproduce the issue on each Smart Proxy, bypassing the load balancer.
Configuring Smart Proxies to use a load balancer results in a more complex environment and requires additional maintenance.
The following additional steps are required for load balancing:
-
You must ensure that all Smart Proxies have the same Content Views and synchronize all Smart Proxies to the same Content View versions
-
You must upgrade each Smart Proxy in sequence
-
You must backup each Smart Proxy that you configure regularly
There are no additional steps required for Smart Proxy servers in a load balancing configuration.
3. Prerequisites for Configuring Smart Proxy servers for Load Balancing
To configure Smart Proxy servers for load balancing, complete the following procedures described in Installing Smart Proxy server. Foreman does not support configuring existing Smart Proxy servers for load balancing.
4. Configuring Smart Proxy servers for Load Balancing
This chapter outlines how to configure Smart Proxy servers for load balancing. Proceed to one of the following sections depending on your Foreman server configuration:
-
Configuring Smart Proxy server with Default SSL Certificates for Load Balancing without Puppet
-
Configuring Smart Proxy server with Default SSL Certificates for Load Balancing with Puppet
-
Configuring Smart Proxy server with Custom SSL Certificates for Load Balancing without Puppet
-
Configuring Smart Proxy server with Custom SSL Certificates for Load Balancing with Puppet
Use different file names for the Katello certificates you create for each Smart Proxy server. For example, name the certificate archive file with Smart Proxy server FQDN.
4.1. Configuring Smart Proxy server with Default SSL Certificates for Load Balancing without Puppet
The following section describes how to configure Smart Proxy servers that use default SSL certificates for load balancing without Puppet.
Complete this procedure on each Smart Proxy server that you want to configure for load balancing.
-
On Foreman server, generate Katello certificates for Smart Proxy server, for example:
# foreman-proxy-certs-generate \ --foreman-proxy-fqdn smartproxy.example.com \ --certs-tar "/root/smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar" \ --foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
Retain a copy of the example
foreman-installercommand that is output by theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand for installing Smart Proxy server certificate. -
Copy the certificate archive file from Foreman server to Smart Proxy server.
# scp /root/smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar \ root@smartproxy.example.com:smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar
-
Append the following options to the
foreman-installercommand that you obtain from the output of theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand. Set the--puppet-ca-serveroption to point to Smart Proxy server where you enter the command. You must install Puppet CA on your Smart Proxy servers, regardless of whether you intend to use it or not. Puppet is configured in its default single-node configuration.--certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, enter the
foreman-installercommand, for example:# foreman-installer --no-enable-foreman \ --foreman-proxy-content-parent-fqdn "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman "true" \ --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key "oauth key" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret "oauth secret" \ --certs-tar-file "smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar" \ --puppet-server-foreman-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
4.2. Configuring Smart Proxy server with Default SSL Certificates for Load Balancing with Puppet
The following section describes how to configure Smart Proxy servers that use default SSL certificates for load balancing with Puppet.
If you use Puppet in your Foreman configuration, you must complete the following procedures:
Complete this procedure only for the system where you want to configure Smart Proxy server to generate and sign Puppet certificates for all other Smart Proxy servers that you configure for load balancing.
In the examples in this procedure, the FQDN of this Smart Proxy server is smart-proxy-ca.example.com.
-
On Foreman server, generate Katello certificates for the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to generate and sign Puppet certificates:
# foreman-proxy-certs-generate \ --foreman-proxy-fqdn smart-proxy-ca.example.com \ --certs-tar "/root/smart-proxy-ca.example.com-certs.tar" \ --foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
Retain a copy of the example
foreman-installercommand that is output by theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand for installing Smart Proxy server certificate. -
Copy the certificate archive file from Foreman server to Smart Proxy server:
# scp /root/smart-proxy-ca.example.com-certs.tar \ root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:smart-proxy-ca.example.com-certs.tar
-
Append the following options to the
foreman-installercommand that you obtain from the output of theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand:--certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, enter the
foreman-installercommand, for example:# foreman-installer --no-enable-foreman \ --foreman-proxy-content-parent-fqdn "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman "true" \ --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key "oauth key" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret "oauth secret" \ --certs-tar-file "smart-proxy-ca.example.com-certs.tar" \ --puppet-server-foreman-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, stop the Puppet server:
# puppet resource service puppetserver ensure=stopped
-
Generate Puppet certificates for all other Smart Proxy servers that you configure for load balancing, except the first system where you configure Puppet certificates signing:
# puppetserver ca generate --certname smartproxy.example.com \ --subject-alt-names loadbalancer.example.com --ca-client
This command creates the following files on the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates:
-
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem -
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/smartproxy.example.com.pem -
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem -
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem
-
-
Resume the Puppet server:
# puppet resource service puppetserver ensure=running
Complete this procedure on each Smart Proxy server excluding the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates.
-
On Foreman server, generate Katello certificates for Smart Proxy server:
# foreman-proxy-certs-generate \ --foreman-proxy-fqdn smartproxy.example.com \ --certs-tar "/root/smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar" \ --foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
Retain a copy of the example
foreman-installercommand that is output by theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand for installing Smart Proxy server certificate. -
Copy the certificate archive file from Foreman server to Smart Proxy server:
# scp /root/smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar \ root@smartproxy.example.com:smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar
-
On Smart Proxy server, install the
puppetserverpackage:# yum install puppetserver
-
On Smart Proxy server, create directories for puppet certificates:
# mkdir -p /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/ \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/
-
On Smart Proxy server, copy the Puppet certificates for this Smart Proxy server from the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates:
# scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem # scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/smartproxy.example.com.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/smartproxy.example.com.pem # scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem # scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem
-
On Smart Proxy server, change the directory ownership to user
puppet, grouppuppetand set the SELinux contexts:# chown -R puppet:puppet /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/ # restorecon -Rv /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/
-
Append the following options to the
foreman-installercommand that you obtain from the output of theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand:--certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "false" \ --puppet-server-ca "false" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, enter the
foreman-installercommand, for example:# foreman-installer --no-enable-foreman \ --foreman-proxy-content-parent-fqdn "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman "true" \ --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key "oauth key" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret "oauth secret" \ --certs-tar-file "smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar" \ --puppet-server-foreman-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "false" \ --puppet-server-ca :false" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
4.3. Configuring Smart Proxy server with Custom SSL Certificates for Load Balancing without Puppet
The following section describes how to configure Smart Proxy servers that use custom SSL certificates for load balancing without Puppet.
4.3.1. Creating Custom SSL Certificates for Smart Proxy server
This procedure outlines how to create a configuration file for the Certificate Signing Request and include the load balancer and Smart Proxy server as Subject Alternative Names (SAN). Complete this procedure on each Smart Proxy server that you want to configure for load balancing.
-
On Smart Proxy server, create a directory to contain all the source certificate files, accessible to only the
rootuser:# mkdir /root/smart-proxy_cert # cd /root/smart-proxy_cert
-
Create a private key with which to sign the Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
Note that the private key must be unencrypted. If you use a password-protected private key, remove the private key password.
If you already have a private key for this Smart Proxy server, skip this step.
# openssl genrsa -out /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy_cert_key.pem 4096
-
Create the certificate request configuration file with the following content:
[ req ] default_bits = 4096 distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name req_extensions = req_ext prompt = no [ req_distinguished_name ] countryName=2 Letter Country Code stateOrProvinceName=State or Province Full Name localityName=Locality Name 0.organizationName=Organization Name organizationalUnitName=Smart Proxy Organization Unit Name commonName=smartproxy.example.com (1) emailAddress=Email Address [ req_ext ] #authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer #basicConstraints=CA:FALSE keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment subjectAltName = @alt_names [alt_names] (2) DNS.1 = loadbalancer.example.com DNS.2 = smartproxy.example.com
-
The certificate’s common name must match the FQDN of Smart Proxy server. Ensure to change this when running the command on each Smart Proxy server that you configure for load balancing. You can also set a wildcard value
*. If you set a wildcard value, you must add the-t foreman-proxyoption when you use thekatello-certs-checkcommand. -
Under
[alt_names], include the FQDN of the load balancer asDNS.1and the FQDN of Smart Proxy server asDNS.2.
-
-
Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for the SAN certificate.
# openssl req -new \ -key /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy_cert_key.pem \ (1) -config SAN_config.cfg \ (2) -out /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy_cert_csr.pem (3)
-
Smart Proxy server’s private key, used to sign the certificate
-
The certificate request configuration file
-
Certificate Signing Request file
-
-
Send the certificate request to the Certificate Authority:
When you submit the request, specify the lifespan of the certificate. The method for sending the certificate request varies, so consult the Certificate Authority for the preferred method. In response to the request, you can expect to receive a Certificate Authority bundle and a signed certificate, in separate files.
-
Copy the Certificate Authority bundle and Smart Proxy server certificate file that you receive from the Certificate Authority, and Smart Proxy server private key to your Foreman server.
-
On Foreman server, validate Smart Proxy server certificate input files:
# katello-certs-check \ -c /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy_cert.pem \ (1) -k /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy_cert_key.pem \ (2) -b /root/smart-proxy_cert/ca_cert_bundle.pem (3)
-
Smart Proxy server certificate file, provided by your Certificate Authority
-
Smart Proxy server’s private key that you used to sign the certificate
-
Certificate Authority bundle, provided by your Certificate Authority
If you set the
commonName=to a wildcard value*, you must add the-t foreman-proxyoption to thekatello-certs-checkcommand.Retain a copy of the example
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand that is output by thekatello-certs-checkcommand for creating the Certificate Archive File for this Smart Proxy server. -
4.3.2. Configuring Smart Proxy server with Custom SSL Certificates for Load Balancing without Puppet
Complete this procedure on each Smart Proxy server that you want to configure for load balancing.
-
Append the following option to the
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand that you obtain from the output of thekatello-certs-checkcommand:--foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
-
On Foreman server, enter the
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand to generate Smart Proxy certificates. For example:# foreman-proxy-certs-generate \ --foreman-proxy-fqdn smartproxy.example.com \ --certs-tar /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.tar \ --server-cert /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ --server-key /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ --server-ca-cert /root/smart-proxy_cert/ca_cert_bundle.pem \ --foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
Retain a copy of the example
foreman-installercommand from the output for installing Smart Proxy server certificates. -
Copy the certificate archive file from Foreman server to Smart Proxy server:
# scp /root/smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar \ root@smartproxy.example.com:smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar
-
Append the following options to the
foreman-installercommand that you obtain from the output of theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand. Set the--puppet-ca-serveroption to point to Smart Proxy server where you enter the command. You must install Puppet CA on your Smart Proxy servers, regardless of whether you intend to use it or not. Puppet is configured in its default single-node configuration.--certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, enter the
foreman-installercommand, for example:# foreman-installer --no-enable-foreman \ --foreman-proxy-content-parent-fqdn "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman "true" \ --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key "oauth key" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret "oauth secret" \ --certs-tar-file "smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar" \ --puppet-server-foreman-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
4.4. Configuring Smart Proxy server with Custom SSL Certificates for Load Balancing with Puppet
The following section describes how to configure Smart Proxy servers that use custom SSL certificates for load balancing with Puppet.
4.4.1. Creating Custom SSL Certificates for Smart Proxy server
This procedure outlines how to create a configuration file for the Certificate Signing Request and include the load balancer and Smart Proxy server as Subject Alternative Names (SAN). Complete this procedure on each Smart Proxy server that you want to configure for load balancing.
-
On Smart Proxy server, create a directory to contain all the source certificate files, accessible to only the
rootuser:# mkdir /root/smart-proxy_cert # cd /root/smart-proxy_cert
-
Create a private key with which to sign the Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
Note that the private key must be unencrypted. If you use a password-protected private key, remove the private key password.
If you already have a private key for this Smart Proxy server, skip this step.
# openssl genrsa -out /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem 4096
-
Create the certificate request configuration file with the following content:
[ req ] default_bits = 4096 distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name req_extensions = req_ext prompt = no [ req_distinguished_name ] countryName=2 Letter Country Code stateOrProvinceName=State or Province Full Name localityName=Locality Name 0.organizationName=Organization Name organizationalUnitName=Smart Proxy Organization Unit Name commonName=smartproxy.example.com (1) emailAddress=Email Address [ req_ext ] #authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer #basicConstraints=CA:FALSE keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment subjectAltName = @alt_names [alt_names] (2) DNS.1 = loadbalancer.example.com DNS.2 = smartproxy.example.com
-
The certificate’s common name must match the FQDN of Smart Proxy server. Ensure to change this when running the command on each Smart Proxy server. You can also set a wildcard value
*. If you set a wildcard value, you must add the-t foreman-proxyoption when you use thekatello-certs-checkcommand. -
Under
[alt_names], include the FQDN of the load balancer asDNS.1and the FQDN of Smart Proxy server asDNS.2.
-
-
Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for the SAN certificate:
# openssl req -new \ -key /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ (1) -config SAN_config.cfg \ (2) -out /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem (3)
-
Smart Proxy server’s private key, used to sign the certificate
-
The certificate request configuration file
-
Certificate Signing Request file
-
-
Send the certificate request to the Certificate Authority:
When you submit the request, specify the lifespan of the certificate. The method for sending the certificate request varies, so consult the Certificate Authority for the preferred method. In response to the request, you can expect to receive a Certificate Authority bundle and a signed certificate, in separate files.
-
Copy the Certificate Authority bundle and Smart Proxy server certificate file that you receive from the Certificate Authority, and Smart Proxy server private key to your Foreman server to validate them.
-
On Foreman server, validate Smart Proxy server certificate input files:
# katello-certs-check \ -c /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ (1) -k /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ (2) -b /root/smart-proxy_cert/ca_cert_bundle.pem (3)
-
Smart Proxy server certificate file, provided by your Certificate Authority
-
Smart Proxy server’s private key that you used to sign the certificate
-
Certificate Authority bundle, provided by your Certificate Authority
If you set the
commonName=to a wildcard value*, you must add the-t foreman-proxyoption to thekatello-certs-checkcommand.Retain a copy of the example
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand that is output by thekatello-certs-checkcommand for creating the Certificate Archive File for this Smart Proxy server.
-
4.4.2. Configuring Smart Proxy server with Custom SSL Certificates for Load Balancing with Puppet
If you use Puppet in your Foreman configuration, then you must complete the following procedures:
Complete this procedure only for the system where you want to configure Smart Proxy server to generate Puppet certificates for all other Smart Proxy servers that you configure for load balancing.
In the examples in this procedure, the FQDN of this Smart Proxy server is smart-proxy-ca.example.com.
-
Append the following option to the
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand that you obtain from the output of thekatello-certs-checkcommand:--foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
-
On Foreman server, enter the
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand to generate Smart Proxy certificates. For example:# foreman-proxy-certs-generate \ --foreman-proxy-fqdn smart-proxy-ca.example.com \ --certs-tar /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy-ca.tar \ --server-cert /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy-ca.pem \ --server-key /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy-ca.pem \ --server-ca-cert /root/smart-proxy_cert/ca_cert_bundle.pem \ --foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
Retain a copy of the example
foreman-installercommand from the output for installing Smart Proxy server certificates. -
Copy the certificate archive file from Foreman server to Smart Proxy server.
-
Append the following options to the
foreman-installercommand that you obtain from the output of theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand:--puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, enter the
foreman-installercommand, for example:foreman-installer --no-enable-foreman \ --foreman-proxy-content-parent-fqdn "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman "true" \ --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key "oauth key" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret "oauth secret" \ --certs-tar-file "certs.tgz" \ --puppet-server-foreman-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "true" \ --puppet-server-ca "true" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, generate Puppet certificates for all other Smart Proxies that you configure for load balancing, except this first system where you configure Puppet certificates signing:
# puppet cert generate smartproxy.example.com \ --dns_alt_names=loadbalancer.example.com
This command creates the following files on the Puppet certificate signing Smart Proxy server instance:
-
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem -
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/smartproxy.example.com.pem -
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem -
/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem
-
Complete this procedure for each Smart Proxy server excluding the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates.
-
Append the following option to the
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand that you obtain from the output of thekatello-certs-checkcommand:--foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
-
On Foreman server, enter the
foreman-proxy-certs-generatecommand to generate Smart Proxy certificates. For example:# foreman-proxy-certs-generate \ --foreman-proxy-fqdn smartproxy.example.com \ --certs-tar /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.tar \ --server-cert /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ --server-key /root/smart-proxy_cert/smart-proxy.pem \ --server-ca-cert /root/smart-proxy_cert/ca_cert_bundle.pem \ --foreman-proxy-cname loadbalancer.example.com
Retain a copy of the example
foreman-installercommand from the output for installing Smart Proxy server certificates. -
Copy the certificate archive file from Foreman server to Smart Proxy server.
# scp /root/smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar \ root@smartproxy.example.com:smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar
-
On Smart Proxy server, install the
puppetserverpackage:# yum install puppetserver
-
On Smart Proxy server, create directories for puppet certificates:
# mkdir -p /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/ \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/
-
On Smart Proxy server, copy the Puppet certificates for this Smart Proxy server from the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates:
# scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem # scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/smartproxy.example.com.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/smartproxy.example.com.pem # scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem # scp root@smart-proxy-ca.example.com:/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem \ /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/public_keys/smartproxy.example.com.pem
-
On Smart Proxy server, change the directory ownership to user
puppet, grouppuppetand set the SELinux contexts:# chown -R puppet:puppet /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/ # restorecon -Rv /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/
-
Append the following options to the
foreman-installercommand that you obtain from the output of theforeman-proxy-certs-generatecommand:--certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "false" \ --puppet-server-ca "false" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
-
On Smart Proxy server, enter the
foreman-installercommand, for example:# foreman-installer --no-enable-foreman \ --foreman-proxy-content-parent-fqdn "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-register-in-foreman "true" \ --foreman-proxy-foreman-base-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "foreman.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-trusted-hosts "smartproxy.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-key "oauth key" \ --foreman-proxy-oauth-consumer-secret "oauth secret" \ --certs-tar-file "smartproxy.example.com-certs.tar" \ --puppet-server-foreman-url "https://foreman.example.com" \ --certs-cname "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-dns-alt-names "loadbalancer.example.com" \ --puppet-ca-server "smart-proxy-ca.example.com" \ --foreman-proxy-puppetca "false" \ --puppet-server-ca "false" \ --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh
5. Installing the Load Balancer
The following example provides general guidance for configuring an HAProxy load balancer on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux server. However, you can install any suitable load balancing software solution that supports TCP forwarding and sticky sessions.
-
On a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 host, install HAProxy:
# yum install haproxy
-
Install the following package that includes the
semanagetool:# yum install policycoreutils-python
-
Configure SELinux to allow HAProxy to bind any port:
# semanage boolean --modify --on haproxy_connect_any
-
Configure the load balancer to balance the network load for the ports as described in Ports Configuration for the Load Balancer. For example, to configure ports for HAProxy, edit the
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgfile to correspond with the table.You must configure sticky session on TCP port 443 to request yum metadata for RPM repositories from different Smart Proxy servers that you configure for load balancing.
Table 1. Ports Configuration for the Load Balancer Service Port Mode Balance Mode Destination HTTP
80
TCP
roundrobin
port 80 on all Smart Proxy servers
HTTPS
443
TCP
source
port 443 on all Smart Proxy servers
RHSM
8443
TCP
roundrobin
port 8443 on all Smart Proxy servers
AMQP
5647
TCP
roundrobin
port 5647 on all Smart Proxy servers
Puppet (Optional)
8140
TCP
roundrobin
port 8140 on all Smart Proxy servers
PuppetCA (Optional)
8141
TCP
roundrobin
port 8140 only on the system where you configure Smart Proxy server to sign Puppet certificates
SmartProxy (Optional for OpenScap)
9090
TCP
roundrobin
port 9090 on all Smart Proxy servers
Docker (Optional)
5000
TCP
roundrobin
port 5000 on all Smart Proxy servers
-
Configure the load balancer to disable SSL offloading and allow client-side SSL certificates to pass through to back end servers. This is required because communication from clients to Smart Proxy servers depends on client-side SSL certificates.
-
Start and enable the HAProxy service:
# systemctl start haproxy # systemctl enable haproxy
6. Registering Clients
You can register a client running a Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 6, 7 or 8 operating system to Smart Proxy servers that you configure for load balancing. For more information about registering clients and configuring them to use Puppet, see Registering Hosts in the Managing Hosts guide.
To register clients, proceed to one of the following procedures:
6.1. Registering Clients Using the Bootstrap Script
To register clients, enter the following command on the client. You must complete the registration procedure for each client.
Ensure that you install the bootstrap script on the client and change the script’s file permissions to executable. For more information, see Registering Hosts to Foreman Using The Bootstrap Script in the Managing Hosts guide.
-
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, enter the following command:
# /usr/libexec/platform-python bootstrap.py \ --login=admin \ --server loadbalancer.example.com \ --organization="Your_Organization" \ --location="Your_Location" \ --hostgroup="Your_Hostgroup" \ --activationkey=your_activation_key \ --enablerepos=https://yum.theforeman.org/client/2.4/el7/x86_64/foreman-client-release.rpm \ --puppet-ca-port 8141 \ (1) --force (2)
-
Include the
--puppet-ca-port 8141option if you use Puppet. -
Include the
--forceoption to register the client that has been previously registered to a standalone Smart Proxy.
-
-
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, 6, or 5, enter the following command:
# python bootstrap.py --login=admin \ --server loadbalancer.example.com \ --organization="Your_Organization" \ --location="Your_Location" \ --hostgroup="Your_Hostgroup" \ --activationkey=your_activation_key \ --enablerepos=https://yum.theforeman.org/client/2.4/el7/x86_64/foreman-client-release.rpm \ --puppet-ca-port 8141 \ (1) --force (2)
-
Include the
--puppet-ca-port 8141option if you use Puppet. -
Include the
--forceoption to register the client that has been previously registered to a standalone Smart Proxy.
-
The script prompts for the password corresponding to the Foreman user name you entered with the --login option.
6.2. Registering Clients Manually
To register clients manually, complete the following procedure on each client that you register.
-
Remove the
katello-ca-consumerpackage if it is installed:# yum remove 'katello-ca-consumer*'
-
Install the
katello-ca-consumerpackage from the load balancer:# rpm -Uvh \ http://loadbalancer.example.com/pub/katello-ca-consumer-latest.noarch.rpm
-
Register the client and include the
--serverurland--baseurloptions:# subscription-manager register --org=Your_Organization \ --activationkey=Your_Activation_Key \ --serverurl=https://loadbalancer.example.com:8443/rhsm \ --baseurl=https://loadbalancer.example.com/pulp/content/
7. Promoting SCAP Content to Clients
The following section describes how to promote Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) content to clients registered to Smart Proxy servers that you configure for load balancing.
-
Ensure that you configure the SCAP content. For more information, see Configuring SCAP Content in Administering Foreman.
-
In the Foreman web UI, navigate to Configure > Classes and click
foreman_scap_client. -
Click the Smart Class Parameter tab.
-
In the pane to the left of the Smart Class Parameter window, click
port. -
In the Default Behavior area, select the Override check box.
-
From the Key Type list, select
integer. -
In the Default Value field, enter
9090. -
In the pane to the left of the Smart Class Parameter window, click
server. -
In the Default Behavior area, select the Override check box.
-
From the Key Type list, select
string. -
In the Default Value field, enter the FQDN of your load balancer. For example,
loadbalancer.example.com. -
In the lower left of the Smart Class Parameter window, click Submit.
-
Add the puppet module that contains the
foreman_scap_clientpuppet class to a Content View. Publish and promote this Content View to your client’s environment. -
If you want to verify the configuration, run the Puppet agent on the client to promote the changes. Do not run the Puppet agent on every client manually because the Puppet agent runs on the clients every 30 minutes.
# puppet agent -t --noop
-
On the client, verify that the
/etc/foreman_scap_client/config.yamlfile contains the following lines:# Foreman proxy to which reports should be uploaded :server: 'loadbalancer.example.com' :port: 9090
-
For more information about Content Views, see Managing Content Views in the Content Management Guide.
8. Verifying the Load Balancing Configuration
You can verify the load balancing configuration by completing the following steps for each Smart Proxy server that you configure:
-
Shut down the base operating system for your Smart Proxy server.
-
Verify that content or subscription management features are available on the client registered to this Smart Proxy. For example, enter the
subscription-manager refreshcommand on the client. -
Restart the base operating system for your Smart Proxy server.